Harold Linke
HITEC Luxembourg S.A.

Ludwig Seitz
Combitech (until 2019 RISE)

Joni Jämsä
CENTRIA University of Applied Sciences

Andreas Ohlsson
Applio Tech AB
While the fusion of cloud, mobile and wireless technologies is one of the biggest business enablers, it is also seen as a major cyber-security challenge. The lack of security technologies that function across such different infrastructures hinders the adoption
of these technologies on the global market, thus limiting the growth potential in this sector.
The three-year CELTIC project CyberWi (2016-2018) created results on security solutions integrating seamlessly over different infrastructures, like Cloud Computing, IoT networks and Embedded Systems, and showed a way towards deployment of commercially viable secure systems that can be implemented in Industrial Internet applications.
CyberWi was a joint undertaking by 13 partners from 3 European countries: Luxembourg, Finland and Sweden.
Approach
In order to ensure that the obtained results work in a production environment, demonstrators and test beds were implemented and publicly presented.
The use cases covered the following topics:
› Building automation, to protect the operation of different sensors and actuators deployed in a building
› Home automation, to protect heterogeneous consumer devices functioning as part of an automated home
› Logistics, to protect the information collected when tracking transports and goods
› Industrial systems, to secure a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system on an oil platform
› Traffic applications, to ensure the safe operation of a traffic signal pre-emption system for emergency services
› Weather services, to ensure road weather station operation as a service hotspot for multiple vehicles
In addition, the development of the OSCORE IETF standard opened the door to progress other lightweight security enablers in areas such as authorization and access control, group communication and authentication. The development of security standards has raised industry interest and led to new collaborations.
Achieved results
CyberWi developed new architectures and standards to improve the security in the above-mentioned use cases. The results have a high commercial impact.
These are some examples:
› The SME Applio (former Q2d Solutions) is now in a go-to-market position with a new software product family developed based on CyberWI results. There are several different commercial IoT solutions about to be implemented. A free and simple IoT service called “Applio Free” has been launched and is in use.
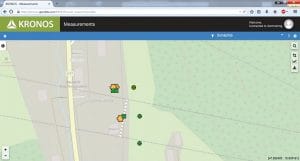
› Road Weather Station – By developing open interfaces the project has conducted road weather stations communication measurements and improved the cybersecurity of wireless connections between the road weather station and the server.
› Hali 2.0 – Traffic Light pre-emption system for emergency vehicles helps municipalities, fire/police departments and hospitals to reach their target faster and safer. Hali is implemented in several Finnish towns with over 700 users.
Further results in standardization and research:
› IETF standards (OSCORE and ACE) for object security and access control in constrained environments (e.g. sensor networks). These standards are integrated into several products. RISE has gained a foothold in the international standardization community at IETF and plans to exploit this in future research projects.
› Open source reference implementations of our proposed standards contributed to commercial open-source libraries implementing the OMA Lightweight M2M standard,
› CyberWi led to the implementation of the Cyber Security Laboratory named SecuLab at the Finnish research institute CENTRIA. SecuLab examines, tests and develops the security of industrial Internet and wireless systems. SecuLab provides tools for system security testing and expertise in information security management to SMEs of the region. It provides expert consulting, whether the company needs an assessment of the information security situation or support for solutions that can be used in company operations.
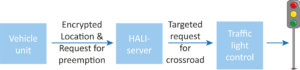
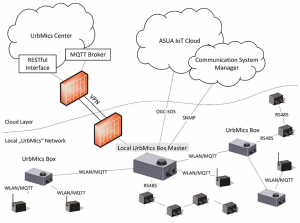
Hali 2.0 overview
Conclusion
The CyberWi project successfully contributed to different R&D topics in the cybersecurity area. A main result is the establishment of a security standard for IoT devices (OSCORE), which is the basis for new additional standards (e.g. Group OSCORE etc). The results of CyberWi are part of several commercial applications and laid the foundation of new services and products.
› Further information
CyberWI project on CELTIC-NEXT website – https://www.celticnext.eu/project-cyberwi/