
© AdobeStock
On 24 March 2022, the European Parliament and the European Council agreed to introduce new EU rules via the Digital Markets Act (DMA) to limit the market power of big online platforms. The DMA will ban certain practices used by large platforms acting as “gatekeepers” and enable the Commission to carry out market investigations and sanction non-compliant behaviour.
The text provisionally agreed by Parliament and Council negotiators targets large companies providing so-called “core platform services” most prone to unfair business practices, such as social networks or search engines, with a market capitalisation of at least 75 billion euro or an annual turnover of 7.5 billion euro. To be designated as “gatekeepers”, these companies must also provide certain services such as browsers, messengers or social media, which have at least 45 million monthly end users in the EU and 10,000 annual business users.
In three-way talks between Parliament, Council and Commission, also known as trilogue, EU lawmakers agreed that the largest messaging services, such as WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger or iMessage, will have to open up and interoperate with smaller messaging platforms upon request. Users of small or big platforms would then be able to exchange messages, send files or make video calls across messaging apps, thus giving them more choice. Regarding interoperability obligations for social networks, co-legislators agreed that such interoperability provisions will be assessed in the future.
The envisage new rules also aim to ensure that combining personal data for targeted advertising will only be allowed with explicit consent given to the gatekeeper. Furthermore, users should be allowed by gatekeepers to freely choose their browser, virtual assistants or search engines.
If a gatekeeper does not comply with the rules, the Commission can impose fines of up to 10% of the gatekeeper’s total worldwide turnover in the preceding financial year, and 20% in case of repeated infringements. In case of systematic infringements, the Commission may ban them from acquiring other companies for a certain time.
The Commission had proposed the Digital Markets Act in December 2020 to address the negative consequences arising from certain behaviours by online platforms acting as digital “gatekeepers” to the EU single market.
Further information
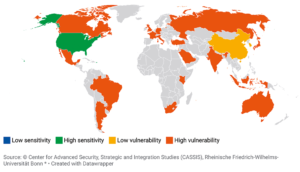





 In January 2024 a new SNS JU funded project was started, called OPTI-6G (Grant Agreement number: 101139292). OPTI-6G develops an optical 6G cell free networks for significantly improved indoor communications. In addition to improved connectivity OPTI-6G will use the developed technology for the very accurate measurement of position and orientation of end user equipment. Advancements provided by OPTI-6G will be showcased in a proof-of-concept demonstrator.
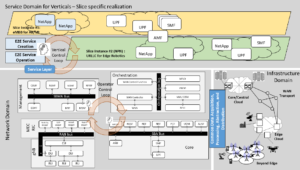
In January 2024 a new SNS JU funded project was started, called OPTI-6G (Grant Agreement number: 101139292). OPTI-6G develops an optical 6G cell free networks for significantly improved indoor communications. In addition to improved connectivity OPTI-6G will use the developed technology for the very accurate measurement of position and orientation of end user equipment. Advancements provided by OPTI-6G will be showcased in a proof-of-concept demonstrator. Eurescom started the ESA 6G SmartSat project together with its subcontractors Airbus Germany GmbH, Deutsche Telekom AG and Fraunhofer FOKUS in January 2024. 6G SmartSat focuses on beyond 5G/6G networking architectures for multi-layered non-terrestrial networks and smart satellites. In this context the project considers the concurrent trends of 5G and beyond 5G NTN, mega-constellations, re-purposable payloads and the concept of multi-layer non-terrestrial networks (ML-NTN), and will assess viable alternatives. The project is planned to conclude in the middle of 2025.
Eurescom started the ESA 6G SmartSat project together with its subcontractors Airbus Germany GmbH, Deutsche Telekom AG and Fraunhofer FOKUS in January 2024. 6G SmartSat focuses on beyond 5G/6G networking architectures for multi-layered non-terrestrial networks and smart satellites. In this context the project considers the concurrent trends of 5G and beyond 5G NTN, mega-constellations, re-purposable payloads and the concept of multi-layer non-terrestrial networks (ML-NTN), and will assess viable alternatives. The project is planned to conclude in the middle of 2025. Horizon Europe INPACE project
Horizon Europe INPACE project As part of a large consortium under the leadership of G.A.C. Group France, Eurescom started a new Horizon Europe support action INPACE – Indo-Pacific-European Hub for Digital Partnerships: Trusted Digital Technologies for Sustainable Well-Being, Grant Agreement number 101135568, in January 2024. The mission of INPACE is to actively support the implementation of the EC Digital Partnerships with Japan, the Republic of Korea, and Singapore, and the cooperation with India in the context of the Trade and Technology Council, by creating a sustainable and interactive multi-stakeholder Indo-Pacific European Hub.
As part of a large consortium under the leadership of G.A.C. Group France, Eurescom started a new Horizon Europe support action INPACE – Indo-Pacific-European Hub for Digital Partnerships: Trusted Digital Technologies for Sustainable Well-Being, Grant Agreement number 101135568, in January 2024. The mission of INPACE is to actively support the implementation of the EC Digital Partnerships with Japan, the Republic of Korea, and Singapore, and the cooperation with India in the context of the Trade and Technology Council, by creating a sustainable and interactive multi-stakeholder Indo-Pacific European Hub. Further information
Further information