Enhancing Data Privacy and Resource Management in Industry through Decentralized AI Solutions
The F4iTECH (Federated AI Platform for Industrial Technologies) project revolutionizes the manufacturing and airport industries by integrating Federated Learning (FL) and advanced AI technologies. Through a decentralized platform, F4iTECH enhances operational efficiency, ensures data privacy and optimizes resource management while addressing hidden challenges and reducing costs. With six pilot implementations showcasing transformative impacts, this innovative approach promises a more intelligent, resilient and sustainable future for industrial environments.
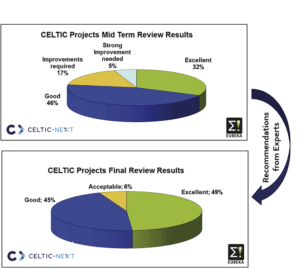
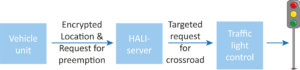
Building on its innovative approach, the F4iTECH project not only improves operational workflows but also tackles critical industry challenges such as data transmission, security and privacy. By leveraging FL-based AI, the platform enables real-time monitoring and decision-making without centralizing sensitive data, thereby enhancing compliance with regulatory frameworks and preserving data sovereignty. The integration of blockchain technology further secures data sharing through smart contracts, fostering collaboration among stakeholders while maintaining individual data ownership. The project’s success is evident in its six pilot implementations, which demonstrated tangible benefits like reduced operational inefficiencies, improved resource allocation, and enhanced resilience in both manufacturing and airport sectors. The Figure 1 shows the system approach and user interaction.
Achieved Results
The project successfully demonstrated significant benefits for the manufacturing and airport industries by integrating FL-based AI into production and operational workflows. A major achievement is the development of FLactionTM, a scalable and privacy-preserving federated learning platform that enables decentralized AI training across multiple edge devices with a user-friendly approach for data scientists. FLactionTM supports seamless model aggregation while ensuring data remains on local devices, addressing privacy concerns and regulatory requirements in industrial applications.
In the airport use case, the project delivered solutions that provide stakeholders with highly accurate, real time predictions of passenger flows for specific time windows. By leveraging advanced machine learning models, these insights enabled airports, airlines, and ground handling services to optimize resource allocation, staffing, and facility management, leading to smoother operations and improved passenger experiences. As a result, the project significantly reduced operational inefficiencies stemming from outdated or inaccurate forecasting methods, minimizing delays, overcrowding, and resource mismanagement. Furthermore, the integration of FL-based AI tackled critical industry challenges, particularly in data transmission, security, and privacy. By enabling decentralized data analysis, the solution eliminated the need for large-scale centralized data repositories, thereby enhancing compliance with stringent regulatory frameworks while also preserving data sovereignty for participating stakeholders. This approach not only ensured the confidentiality of sensitive passenger information but also fostered greater collaboration among stakeholders by allowing them to access valuable insights without compromising individual data ownership.
The results of the project are expected to have a lasting impact on different sectors, enhancing operational efficiency, reducing costs and improving stakeholder collaboration. The technologies developed may serve as a foundation for new product developments, standardization efforts, and further research. Additionally, the outcomes of the project, including methodologies and findings, have the potential for publication in major papers, fostering wider adoption and refinement of FL-based AI in industry applications.
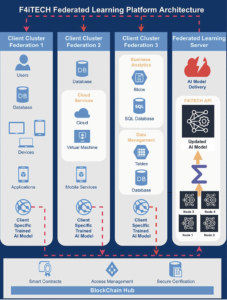
Figure 1: F4iTECH Federated Learning Platform Architecture
Impact
F4iTECH delivers significant benefits to the manufacturing, retail and airport industries by seamlessly integrating FL-based AI solutions into industrial processes. Utilizing distributed ledgers, the project securely records all relevant events and transactions within the Industry 4.0 ecosystem, enabling stakeholders and end consumers to intuitively verify data and establish smart contracts. Through systematic AI-driven predictive maintenance and machinery inspection, F4iTECH enhances equipment performance and reduces deterioration rates by 20%. By addressing and resolving hidden operational challenges, the project aims to cut invisible and internalized costs by 15%, contributing to more efficient and cost-effective industrial environments.
Conclusion
The F4iTECH project demonstrates how Federated Learning (FL) and advanced AI technologies can transform industrial sectors by enhancing operational efficiency, data privacy, and resource management. The project’s decentralized approach not only solves hidden challenges but also reduces costs and improves resilience. Future projects/products could build on F4iTECH’s methodologies to explore broader applications of FL-based AI in other industries, advancing data-driven innovation while maintaining stringent privacy standards.
For more information, visit:
https://www.celticnext.eu/project-f4itech/