
Eurescom contributes to ESA workshop regarding the convergence of 5G communication and Earth Observation
The 5th ESA Workshop on Advanced Flexible Telecom Payloads was held at ESA’s European Centre for Space Applications and Telecommunications (ECSAT) at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in the UK, between the 18 and 20 March 2025. Over 100 experts from across Europe participated at the workshop. Adam Kapovits from Eurescom has contributed to the workshop session on Flexible Payloads for 5G/6G NTNs with the results from the ESA project 5GEOSiS – 5G Earth Observation Server in Space, a 5G repurposable payload as a service, and received very positive feedbacks from the audience.

ESA NICT workshop held in Tokyo at the NICT Innovation Center on 31st March 2025
The European Space Agency and the National Institute of Information And Communications Technology Japan first signed a Letter of Intent (LoI) in 2018 regarding joint efforts and cooperation in the field of 5G satellite communications.
Subsequently, the two sides supported their own industries launching investigations as technology path finders for global satellite communication networks convergence, integration into 5G and to validate use cases of common interest, such as natural disaster prevention and mitigation, global maritime transportation, and Internet of Things (IoT) to cover oceans and airspaces.
These activities were performed on the European side as part of the ESA SATis5 project (funded within ESA’s Space for 5G/6G and Sustainable Connectivity portfolio) under the leadership of Eurescom GmbH and with the assistance of Fraunhofer FOKUS as technical manager, and together with the Japanese industrial team under the leadership of Japan Radio Co., Ltd, and with SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation and the University of Tokyo as partners.
On 31stMarch 2025 a half a day workshop was held between the European and Japanese teams when the experts from the two sides and from the funding agencies (ESA and NICT, respectively) met to discuss the key results of the trials that resulted from the collaboration, the lessons learnt and technical areas of interest for continuing the collaboration.
The collaboration was organised in phases. In the first phase industry partners worked on the interconnection of local 5G systems via satellite, as well as the management of long-distance networks between Europe and Japan.The teams achieved a network quality evaluation of satellite and 5G connection, working to understand the feasibility of satellite 5G networks via international long-distance communications, as well as the successful transmission of 4K Video and IoT Data.
In a second phase multi-orbit (geostationary (GEO) / low Earth orbit (LEO)) 5G transport solutions were investigated and validated, and the multi-5G-Core enhancements that are necessary and typical in international communications. These topics were introduced and are now being discussed in 3GPP Rel 19/20.
In this phase, the European team concentrated on links performance monitoring; dynamic path selection between GEO-LEO-Terrestrial networks; and data path management. Meanwhile, the Japanese team concentrated on network slicing, Quality of Service, active bandwidth control and application detection in switching GEO-LEO-Terrestrial link scenarios.
Technical achievements from European partners included experimenting and validating services in Public Protection and Disaster Relief (PPDR) fire-fighting scenarios with 5G temporary local networks interconnected via satellite, including User Equipped UAVs for video monitoring. Experimentation taking place in Berlin, Brandenburg area in Germany.
Additionally, the Japanese team showcased their experimentation and validation of PPDR use cases utilizing Non-Public 5G networks over satellite, such as 4K video footage viewed through Virtual Reality lenses, remote control of field-deployed robot via video transmission, and various applications for remote areas.
Overall, the European and Japanese Phase 2 trials confirmed the feasibility of real-time switching of multi-orbit satellite links, and the associated network components and applications sessions. Additionally, the Over the Air validation trials demonstrated the feasibility of seamless path switching.
Looking forward, both the European and Japanese side investigates how the collaboration could be continued and extended towards Beyond 5G and 6G Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN).
 Further information
Further information
- “Advanced Flexible Telecom Payloads Event” – Nikal Events. Available at: https://nikal.eventsair.com/advanced-flexible-telecom-payloads/
- “5GEOSIS – 5G Earth Observation Server in Space” – ESA Connectivity. Available at: https://connectivity.esa.int/projects/5geosis-%E2%80%93-5g-earth-observation-server-space

ESA NICT workshop participants form the European and Japanese partners at the NICT Innovation Center in Tokyo, on 31st March
From left to right: Yuma Abe, NICT, Natsuko Ouchi, SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation, Nobuyuki Setoguchi, SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation, Sachie Tsubokura, Japan Radio Co., Ltd, Atsumu Mishima, SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation, Marius Iulian Corici, Fraunhofer FOKUS, Shinichi Mizuno, Japan Radio Co., Ltd, Bjoern Riemer, Fraunhofer FOKUS, Adam Kapovits, Eurescom GmBH, Maria Guta, ESA, Prof Akihiro Nakao, The University of Tokyo, Kenji Kanai, The University of Tokyo, Amane Miura, NICT, Katsuyoshi Ishida, Japan Radio Co., Ltd, Kiyomi Yoshida, Japan Radio Co., Ltd, Keita Kaida, The University of Tokyo, Mayuko Tsuji, Japan Radio Co., Ltd, Yoji Oshima, The University of Tokyo.


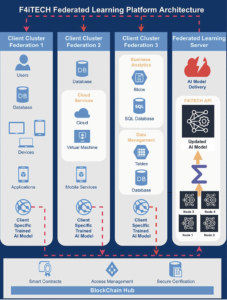







 Eurescom, as the prime coordinator of the 6G SmartSat ESA project, has released the white paper “Topology Semantic Routing for Mega-Constellations,” developed with Fraunhofer FOKUS, Airbus Defence and Space, and Deutsche Telekom. The paper introduces Topology Semantic Routing (TSR), an innovative solution for the dynamic routing challenges faced by Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) in LEO and MEO mega-constellations, where traditional protocols like OSPF and BGP fall short. TSR offers adaptive, real-time routing with minimal satellite compute load, using local information and pre-computed paths to maintain network resilience and efficiency without extensive signalling. It integrates with centralized routing models, supporting seamless 5G TN-NTN convergence, and addresses trade-offs between signalling and memory use. Future validation with OpenLANES will enhance its commercial readiness, marking a major step toward advancing multi-sector 6G satellite network applications.
Eurescom, as the prime coordinator of the 6G SmartSat ESA project, has released the white paper “Topology Semantic Routing for Mega-Constellations,” developed with Fraunhofer FOKUS, Airbus Defence and Space, and Deutsche Telekom. The paper introduces Topology Semantic Routing (TSR), an innovative solution for the dynamic routing challenges faced by Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) in LEO and MEO mega-constellations, where traditional protocols like OSPF and BGP fall short. TSR offers adaptive, real-time routing with minimal satellite compute load, using local information and pre-computed paths to maintain network resilience and efficiency without extensive signalling. It integrates with centralized routing models, supporting seamless 5G TN-NTN convergence, and addresses trade-offs between signalling and memory use. Future validation with OpenLANES will enhance its commercial readiness, marking a major step toward advancing multi-sector 6G satellite network applications.


 The Test, Measurement, and KPIs Validation (TMV) Working Group (WG) of SNS JU focuses on developing and sharing best practices for 6G testing, monitoring, and analytics. The TMV WG aims to promote common methodologies across projects, support 6G trial Use Cases (UCs), and ensure a unified European vision for the 6G network lifecycle. A key objective is the definition and validation of performance KPIs. This white paper consolidates 6G KPIs from SNS JU projects, providing definitions, target values, and context to shape the 6G vision. Furthermore, the TMV WG promotes common collection procedures, validation methodologies, and analysis of KPI metrics. Various SNS JU projects provided the KPIs, which drive their technical developments.
The Test, Measurement, and KPIs Validation (TMV) Working Group (WG) of SNS JU focuses on developing and sharing best practices for 6G testing, monitoring, and analytics. The TMV WG aims to promote common methodologies across projects, support 6G trial Use Cases (UCs), and ensure a unified European vision for the 6G network lifecycle. A key objective is the definition and validation of performance KPIs. This white paper consolidates 6G KPIs from SNS JU projects, providing definitions, target values, and context to shape the 6G vision. Furthermore, the TMV WG promotes common collection procedures, validation methodologies, and analysis of KPI metrics. Various SNS JU projects provided the KPIs, which drive their technical developments.
 The Smart Networks and Services Joint Undertaking (SNS JU), under Horizon Europe, is advancing Europe’s leadership in 6G by integrating AI and ML into future networks. A survey of 33 projects revealed 199 AI/ML-based mechanisms focused on RAN, resource management, diagnostics, and energy efficiency, mainly using supervised learning and deep learning methods. Projects rely on synthetic, real, and mixed datasets, with outputs targeting radio optimization, security, and resource management. Trends like Explainable AI (XAI) and privacy-preserving techniques such as federated learning are gaining importance. Through these efforts, SNS JU is laying the foundation for AI-native 6G networks while promoting ethical, sustainable innovation and reinforcing Europe’s technological sovereignty.
The Smart Networks and Services Joint Undertaking (SNS JU), under Horizon Europe, is advancing Europe’s leadership in 6G by integrating AI and ML into future networks. A survey of 33 projects revealed 199 AI/ML-based mechanisms focused on RAN, resource management, diagnostics, and energy efficiency, mainly using supervised learning and deep learning methods. Projects rely on synthetic, real, and mixed datasets, with outputs targeting radio optimization, security, and resource management. Trends like Explainable AI (XAI) and privacy-preserving techniques such as federated learning are gaining importance. Through these efforts, SNS JU is laying the foundation for AI-native 6G networks while promoting ethical, sustainable innovation and reinforcing Europe’s technological sovereignty. The Women in Telecommunications and Research (WiTaR) Working Group is proud to present its 2024 Yearly Report. This report provides a snapshot of our efforts to promote the participation and advancement of women in telecommunications. Despite remarkable technological progress, the ICT industry still faces significant gender disparities, with women comprising less than 30% of the workforce globally and even lower representation in technical and leadership roles. These gaps limit diversity, hinder innovation, and reduce the sector’s potential. In 2024, WiTaR worked tirelessly to address these challenges through fostering inclusive workplace cultures, supporting mentorship and leadership development, and driving diversity-forward initiatives. Our activities this year reflect our ongoing commitment to building a more equitable ICT ecosystem.
The Women in Telecommunications and Research (WiTaR) Working Group is proud to present its 2024 Yearly Report. This report provides a snapshot of our efforts to promote the participation and advancement of women in telecommunications. Despite remarkable technological progress, the ICT industry still faces significant gender disparities, with women comprising less than 30% of the workforce globally and even lower representation in technical and leadership roles. These gaps limit diversity, hinder innovation, and reduce the sector’s potential. In 2024, WiTaR worked tirelessly to address these challenges through fostering inclusive workplace cultures, supporting mentorship and leadership development, and driving diversity-forward initiatives. Our activities this year reflect our ongoing commitment to building a more equitable ICT ecosystem.
 The telecommunications industry is adapting to new business dynamics introduced by 5G and preparing for similar challenges expected with 6G. Recognizing the importance of aligning technological advances with value creation, the 6G Industry Association (6G-IA) sub-working group Business Validation, Models, and Ecosystems (BVME-SG) has released a new white paper building on its previous work on 5G/B5G ecosystem business modeling. Using the Industry 4.0 vertical as an example, the paper applies a five-step framework to help stakeholders identify business opportunities and understand how ecosystem variations impact operations and strategy. It further explores the cost implications of ecosystem configurations, suggesting new methods for evaluating the technoeconomic viability of networks on a per-deployment and per-actor basis. Finally, the paper discusses the evolving roles within the 6G ecosystem, noting that, although 6G networks will be even more distributed and disaggregated than 5G, the same business modeling framework remains highly relevant for the transition.
The telecommunications industry is adapting to new business dynamics introduced by 5G and preparing for similar challenges expected with 6G. Recognizing the importance of aligning technological advances with value creation, the 6G Industry Association (6G-IA) sub-working group Business Validation, Models, and Ecosystems (BVME-SG) has released a new white paper building on its previous work on 5G/B5G ecosystem business modeling. Using the Industry 4.0 vertical as an example, the paper applies a five-step framework to help stakeholders identify business opportunities and understand how ecosystem variations impact operations and strategy. It further explores the cost implications of ecosystem configurations, suggesting new methods for evaluating the technoeconomic viability of networks on a per-deployment and per-actor basis. Finally, the paper discusses the evolving roles within the 6G ecosystem, noting that, although 6G networks will be even more distributed and disaggregated than 5G, the same business modeling framework remains highly relevant for the transition.
 This white paper has been prepared by the 6G Architecture working group of the Smart Network and Services Joint Undertaking (SNS JU). It presents a comprehensive snapshot of the current architectural considerations explored by the SNS JU projects. It discusses the rationale for novel architectural components, the ongoing design efforts, and the future outlook for 6G. It analyses the blueprint for next-generation mobile networks, building on past experiences while integrating cutting-edge advancements. The structure follows the IMT-2030 framework, categorizing insights into the key usage scenarios and overarching architectural aspects.
This white paper has been prepared by the 6G Architecture working group of the Smart Network and Services Joint Undertaking (SNS JU). It presents a comprehensive snapshot of the current architectural considerations explored by the SNS JU projects. It discusses the rationale for novel architectural components, the ongoing design efforts, and the future outlook for 6G. It analyses the blueprint for next-generation mobile networks, building on past experiences while integrating cutting-edge advancements. The structure follows the IMT-2030 framework, categorizing insights into the key usage scenarios and overarching architectural aspects.





 Further information
Further information
