Enabling the faster convergence and development of terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks & services
On 22 November 2021, Eureka Cluster CELTIC-NEXT and the European Space Agency (ESA) signed a Memorandum of Intent (MoI) in Porto, Portugal, which aims to bring their respective communities closer together. The MoI will help to foster economic growth and jobs through coordinated R&D&I activities and the commercial exploitation of integrated space and terrestrial systems enabled by 5G and 6G. The collaboration aims to leverage the complementarity of ESA and CELTIC-NEXT and build on synergies to maximise the return on investment and to support achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
In today’s rapidly changing political and economic environment and its regional battlefields, Space ICT has become, more than ever, a pillar for sovereignty and resiliency.
Space ICT is currently at the centre of attention for global industry and governments. On the economic side, new non-European entrants are currently disrupting the sector with Low-Earth-Orbit (LEO) satellites and High-Altitude Pseudo-Satellites (HAPS). On the political side, satellites, with all their potential missions and services, have shown to be essential assets for countries, not only for media broadcasting and observation, but also for connectivity to individuals and objects.
European industry and countries must defend their economic and political shares in Space ICT. European industry must be able to support European countries’ ICT & data sovereignty. Sovereignty cannot be achieved by purchasing and deploying equipment and services from foreign vendors that could fall under or are already under control of non-trustable governments.
Recent events in Eastern Europe have shown, how critical it is to count on both terrestrial and non-terrestrial ICT services, as together they constitute one of the critical infrastructures of a country, especially considering the digitalisation of the society and the vertical industries.
Therefore, it is mandatory to increase and leverage to its maximum the European and allied countries’ funding to reach the critical mass for R&D&I and a faster time-to-market for the European countries and allies’ ICT industry.

Eureka Chairman Miguel Bello Mora, Elodie Viau – Director of Telecommunications and Integrated Applications and Head of ECSAT at the European Space Agency (ESA), and CELTIC Office Director Xavier Priem
The central role of space and satellites
Space, satellites and alike play an extended and increasingly critical role in 5G, 6G and overall ICT services enabling the digital society.
Space and satellites had already an important role in the global ICT world for the economy, industry, and the people. They have already provided media broadcasting (TV), geo-positioning (GPS, GONASS, etc.), data links (backhauling and access), and telephony (satellite phones). For data links and telephony, they were mainly meant to provide those services in areas not well or at all covered by terrestrial networks, and recently also where high-data capacity was not needed. LEO fleets have somehow changed this perception by providing high-peak capacity over the coverage of one LEO satellite, with the foreseeable de-facto limitation of the maximum number of simultaneously attached users, as those share the same total LEO satellite bandwidth.
Since 5G and reinforced with 5G-Advanced, and the planned 6G, more industry verticals are getting digitalised, automated and autonomised, wireless connected instead of wired connected, or simply “connected”. People will expect that services delivered by those vertical industry sectors will be ubiquitous, always on and resilient. A good example is Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAV), being cars, trucks, terrestrial drones but also flying objects like future flying taxis, delivery drones, and more. 3GPP has now opened wider doors for the inclusion of SatCom besides the traditional backhauling role.
Space ICT remains a complex field with specifics in terms of operational conditions for R&D&I as well as field deployment.
Entry barriers to the Space ICT sector
Several factors create an often too high barrier to entry for new or small players originating from the terrestrial ICT sector to move their technologies and products to the space or third dimension:
› The specific space environment for radiations, dimensions and weight, power supply limitations (level and duration) implying very costly special hardware platforms, if they even exist
› The satellites‘ launch costs
› The inherent inaccessibility after launch in case of outages or upgrades poses challenges not existing for terrestrial network players
› And, moreover, the space and satellite technologies (platform, payload, antennas…) knowledge itself
For the existing actors from the space sector, they seek for more competencies in 3GPP technologies and closer integration with terrestrial actors.
What CELTIC-NEXT and ESA bring to the collaboration
ESA TIA ARTES and CELTIC-NEXT provide various funding instruments: Open Calls, ITT, PPP for ESA, and bottom-up, flagship and joint ECP calls for CELTIC-NEXT. By exposing those instruments to each other’s community and together, both organisations will provide a privileged forum for cross-fertilisation and collaboration of both communities, leveraging the different TRLs, funding schemes and public funding agencies across the large sum of their respective geographical coverages: the Eureka countries for CELTIC and the ESA countries, some being common and some being different. Some stakeholders are common to ESA and CELTIC-NEXT, but most are new to the other. Both organisations see high complementarity in joining forces to leverage the association of their respective assets, forces, and communities.
As Elodie Viau said at the MoI Signature ceremony in Porto: “ESA`s strategic programme line Space for 5G & 6G demonstrates the essential nature of satellites for 5G and 6G. It sets the standards and frameworks for systems and services interoperability, as well as the base for integrating terrestrial networks with satellites. We draw technology and product roadmaps; we support and foster the development of integrated satellite terrestrial systems and value-added services.”
What this collaboration will enable and what it will target
This MoI and the attached collaboration will enable the faster convergence and development of terrestrial and non-terrestrial network and service technologies in the innovative field of Space ICT, i.e., three-dimensional networking.
The MoI will focus on technology pathfinders and solutions to develop and validate research & development projects initiated by ESA and CELTIC-NEXT. In addition, the MoI includes the organisation of joint events as well as the dissemination of relevant information to terrestrial, non-terrestrial, and combined operators and vertical market stakeholders.
More specifically, the MoI will encourage terrestrial ICT and Space ICT industry collaboration with other industry verticals to facilitate the adoption of advanced Space ICT technologies in the business models and processes of all industry sectors. The focus of the cooperation is to consider the issues in a holistic way by considering the end-to-end perspective of new communications services enabled by 5G and 6G technologies, including an understanding of the economic, environmental, and societal benefits.
How it will be implemented
In a first phase, each organization will run its own funding instruments, with its own processes. This cooperation does not replace their respective funding programmes and instruments, but leverages them for identified synergies in terms of topics of interest or strategic goals for their communities.
Coordination on specific themes will be put in place. These themes, include, but are not limited to:
› Multi-layered Space ICT and Flying Objects Convergence
› Design and development of systems, subsystems and technology
› Networks and services conformance and interoperability tests
› Viable business ecosystem models
› Convergence and integration of terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks
› Frequency spectrum sharing between satellite networks and other satellite/terrestrial networks
› Network timing and synchronisation technologies
› Edge cloud computing
› Data driven (AI enabled) management
› Data curation technologies
› Digital twins
To support the achievement of their common objectives, the two organisations intend to:
› Share knowledge, ideas and lessons learned
› Create awareness and promote opportunities for collaboration
› Utilise and leverage their relevant resources and expertise necessary to ensure the success of the common objectives, in support of the activities initiated in the context of this cooperation
› Plan and manage jointly relevant activities in areas of common interest in line with the signatories’ respective legal frameworks
› Collaborate on the organisation and execution of activities with a view to reaching the common objectives identified
› Regularly attend meetings concerning the effectiveness of the collaboration, with reference to the priorities agreed
› Participate in suitable events organized by the other signatory
› Undertake joint communication, as appropriate, addressing the cooperation domains
Joint actions will be developed such as:
› Roadmapping
› Joint cross-community technology and strategy advisory boards
› Exchange on call dates and processes to anticipate best conditions for calls and participants
› Knowledge network creation and animation
› Joint working groups on specific topics across funded projects
› Joint webinars and workshops
› Promotion and provision of testbeds and trials platforms (R&D, integration, launch)
› Mutual advertisement of calls and bringing communities to jointly apply
The strategic technology calls and actions roadmaps are currently under development. CELTIC-NEXT is happy to receive your input and feedback to enrich its contribution to the joint work.
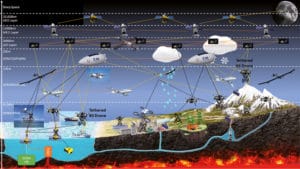
The new Space-ICT Programme – Targeting the global 3D Internet
Outlook
This MoI is the first of a series of new collaborations for CELTIC-NEXT. This fulfils the objectives set by CELTIC-NEXT’s Core Group to develop CELTIC-NEXT’s support to and impact for the ICT community by enriching its DNA with new verticals and communities. The space community is also eager to collaborate more with the terrestrial ICT community. This collaboration offers the perfect playground for both communities to meet and work together on strategic topics and projects. CELTIC-NEXT welcomes greatly the space community’s contribution to this strategic programme in terms of inputs to the roadmaps, participation to joint events and meetings, and proposals in the coming Space-ICT and 3D-NET focused calls to be announced soon.





