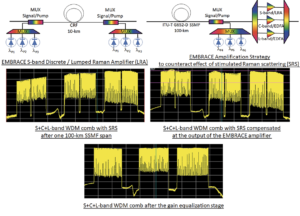
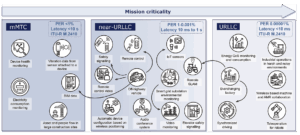
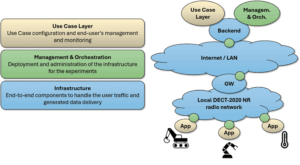
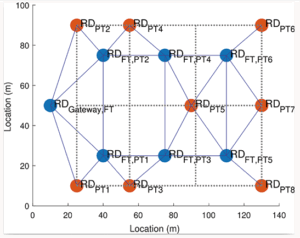
What CELTIC-NEXT Cluster has delivered in the first half of 2025
and what is coming next?

Xavier Priem
Director CELTIC Office
What CELTIC-NEXT Cluster has delivered in the second half of 2025
and what is coming in 2026.
For CELTIC-NEXT, 2025 was a year of renewal. The second EUREKA Clusters’ Programme (ECP) Arrangement was signed at the beginning of June 2025, with an effective start date of 1 July 2025. CELTIC-NEXT’s EUREKA Cluster’s License has been renewed for the next seven years with the strong support from the EUREKA Countries’ Network!
Let’s review what was achieved in 2025 and what we are currently planning for 2026.
2025 achievements:
On June 12, 2025, I had the honour of defending our CELTIC-NEXT application for a renewed license to operate as EUREKA Cluster. We received a clear positive vote from all voting countries, with a single exception (abstention). Beyond the quality of our application, it is the high-quality work of our community and our Office that has received this highest recognition from the EUREKA Network. The EUREKA Countries place seven years of renewed trust in us. We can now build on those seven years to develop a powerful new phase of CELTIC-NEXT: a revised and broader SRIA, improved and simplified processes, and expanding our presence across more countries, including beyond European borders (Canada, Brazil, Chile, Singapore, etc.).
Our intense engagement in the overall EUREKA Clusters Programme (ECP) will continue following three principal axes:
1. Pursuing the lead role on the writing of the ECP Processes Handbook, working with the other clusters and the Public Authorities. This work is essential as it will define more harmonised processes between clusters and public authorities to address the current challenges of the ECP, such as the time it takes to start a project after it has been labelled.
2. Implementing the requested changes in our CELTIC-NEXT processes and tools to reflect on point nr. 1.
3. Coordinating Clusters’ contributions to the ECP, with CELTIC-NEXT’s Director as Clusters Coordinator for the Industry side.
2025 saw the transition from the Canada-Germany Presidency to the Switzerland Presidency
Thank you, Canada and Germany!

Eureka Chair Handover Ceremony: from Germany & Canada Presidency to Switzerland Presidency
The EUREKA Network was co-presided over by Canada and Germany from July 2024 to June 2025. Switzerland has now taken over for the current EUREKA year, from July 1, 2025, to June 30, 2026. CELTIC-NEXT’s Director’s assignment as Clusters Coordinator Industry spans over the same period.
In the name of CELTIC-NEXT, I would like to thank Canada and Germany for their outstanding leadership and support in achieving the significant step of renewing the ECP and the five Clusters licenses. This work has exposed CELTIC-NEXT to the Canadian Public Authority Representatives more deeply, which leads us to jointly plan an increased participation of Canadian entities (SMEs mainly) in our cluster’s bottom-up calls and flagships.
Welcome Switzerland!
From 1 July 2025 to 30 June 2026, Switzerland, represented by the innovation funding agency Innosuisse, assumes EUREKA’s Chair. This leadership role coincides with a major milestone: EUREKA’s 40th anniversary. In this capacity, the Swiss Chair has outlined an ambitious agenda, built around three forward-looking priorities:
1. Strengthening collaboration: among EUREKA’s beneficiaries, members, and partner organisations;
2. Amplifying impact: showcasing successes and shaping the future funding portfolio, and,
3. Empowering beneficiaries: through improved support and operational excellence.
More about Swiss Chair priorities and events under https://www.eurekanetwork.org/about-us/chair/
2025-2026 Running/Upcoming Calls
The Spring Call 2025 was a success, with nineteen valid proposals, from which eleven got labelled and are in the ramp-up phase. It is still possible to join some of these projects while they are ramping up. Please visit https://www.celticnext.eu/running-projects/ for more information.
When this edition of the CELTIC-NEXT’s News is published, the Autumn Call 2025 would have closed (deadline 24 October 2025). Therefore, it is already time to announce the Spring Call 2026!
The Spring Call 2026 will be launched at the beginning of December 2025 in an online event. The Proposers’ Brokerage Day will take place in person at the end of January or the beginning of February 2026, probably in Brussels/Belgium (to be confirmed). The precise date and location will be announced via our Newsletter and our website. The full project proposals’ submission will close on April 24, 2026, for a labelling decision before mid-June 2026. The forecasted possible start period for labelled projects would then be the second half of 2026.
A new, updated SRIA will enable future successful innovation support and change.
We are still collecting updates from our community on our Strategic Research and Innovation Roadmap (SRIA), which we are currently refining. We will incorporate this new SRIA in our Launch Events and Proposers’ Brokerage Days in 2026, to allow consortia to propose innovative projects in a more extensive variety of technologies, services, applications, and verticals. This reinforces our traditional bottom-up approach. We will continue to run our Spring and Autumn Calls based on this successful legacy. Bottom-up approach is a unique selling point of CELTIC-NEXT as an EUREKA Cluster compared to other international funding schemes (top-down approach). Please contact me () if you wish to contribute.
Flagships
SUSTAINET is running!
The new flagship, SUSTAINET, was labelled for its initial application in June 2024. Its central theme is network resilience, energy efficiency, sustainability, high-performing end-to-end networks, and network security. In the meantime, SUSTAINET and its three sub-projects have kicked-off. Despite being in the ramp-up phase, SUSTAINET has already begun its dissemination work, notably by attending several events like Hannover Messe and the ICOC 2025 Conference.
Canadian companies have now also joined SUSTAINET, extending its boundaries beyond Europe.
The CELTIC-NEXT office is happy to connect with potential new partners interested in joining the flagship during this first phase. Please contact us at office@celticnext.eu or directly the SUSTAINET Consortium .
3D-NET is ramping up!
The Spring Call 2021 project 6G-SKY concluded this summer 2025, marking a great success. It’s leading partner, Airbus Defence & Space, together with KTH and several participants from 6G-SKY, successfully applied in the Spring Call 2025 and have been granted a new labelled project, called 3D-NET. 3D-NET is the seed of a future flagship strand on Airspace/Non-Terrestrial and Terrestrial Networks convergence. Don’t hesitate to get in touch with us at .
Acquiring new Core Group memberships
The director of CELTIC-NEXT has the mandate from CELTIC-NEXT’s Core Group to propose and integrate new industry members into the existing Core Group. Discussions are ongoing with several industrial companies.
Outlook into 2026
The new ECP is signed to last seven years, providing the EUREKA Clusters with extended visibility into the future and, therefore, elaborating a stronger path for growth.
2026 will be the year of the new EUREKA Clusters Programme (ECP) ramp-up and more detailed implementation.
2026 will be a year of improvement; Optimization and simplification of processes to increase the programme’s efficiency, reducing delays from ideation to proposal submission, evaluation and finally to funding (incl. its synchronisation).
2026 will be a year of growth, starting with the renewed trust and support of existing partnering Public Authorities, and new incoming funding countries, such as Lithuania, Chile, and Brazil.
Finally, in 2026, an increased collaboration with Canada will take place. We have initiated discussions on how to facilitate Canada’s participation in CELTIC-NEXT brokerage events. This means that we will integrate this into our event planning, as it requires time to assemble such delegations to travel to Europe.
Further information
Stay tuned by visiting our Call Calendar page: https://www.celticnext.eu/call-calendar/ and/or by subscribing to our
Newsletter under https://www.celticnext.eu/news-subscription/

 The first keynote gave insights “on the path to the AI-ACT”, kindly presented by Prof. Diogo Gomes from Instituto de Telecomunicações.
The first keynote gave insights “on the path to the AI-ACT”, kindly presented by Prof. Diogo Gomes from Instituto de Telecomunicações. Wolfgang John provided insights on how AI-native networks, 6G Compute, Trustworthy systems and limitless connectivity capabilities of the 6G network platform serve as key enablers for co-creating a cyber physical world. First ideas on AI powered services have been shown working on today’s but also on tomorrows mobile networks that are both a communication and a computing platform.
Wolfgang John provided insights on how AI-native networks, 6G Compute, Trustworthy systems and limitless connectivity capabilities of the 6G network platform serve as key enablers for co-creating a cyber physical world. First ideas on AI powered services have been shown working on today’s but also on tomorrows mobile networks that are both a communication and a computing platform.